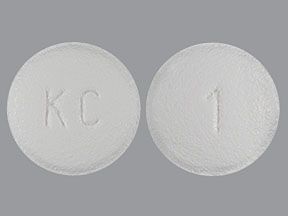
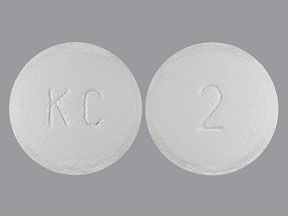
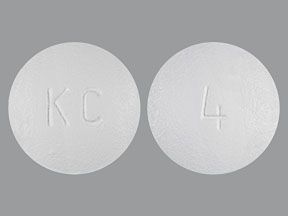
Livalo (pitavastatin) is a prescription drug that’s used to lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels. The drug comes as an oral tablet. It’s usually taken once per day.
Livalo is prescribed along with diet to lower LDL cholesterol levels in:
- adults with primary hyperlipidemia
- adults and some children with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia
Livalo belongs to a group of drugs called statins. Its active ingredient is pitavastatin. (An active ingredient is what makes a drug work.)
Livalo comes as a tablet that you swallow.
This article describes the dosages of Livalo, as well as its strengths and how to take it. To learn more about Livalo, see this in-depth article.
The table below highlights dosage basics for Livalo. All dosages are listed in milligrams (mg).
| Condition | Dosage range | Maximum dosage |
| primary hyperlipidemia | 2–4 mg per day | 4 mg per day |
| heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia | 2–4 mg per day | 4 mg per day |
What is Livalo’s form?
Livalo comes as a tablet that you swallow.
What strengths does Livalo come in?
Livalo comes in three strengths: 1 mg, 2 mg, and 4 mg.
What are the usual dosages of Livalo?
Your doctor will likely start you on a low dosage and adjust it over time to reach the right amount for you. They’ll ultimately prescribe the smallest dosage that provides the desired effect.
The information below describes dosages that are commonly used or recommended. But be sure to take the dosage your doctor prescribes for you. They’ll determine the best dosage to fit your needs.
Dosage for high cholesterol
The dosage range for Livalo is typically 2–4 mg per day. Your doctor will likely start you on the 2-mg tablet of Livalo once per day.
After 4 weeks, your doctor will check your cholesterol levels. If your levels are still high, your doctor may increase your dose.
The maximum dosage of Livalo is 4 mg per day.
What’s the dosage of Livalo for children?
Livalo can be used to treat heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia in children ages 8 years and older.
The dosages prescribed for children are the same as those prescribed for adults.
The dosage range is 2–4 mg per day. The usual starting dose is 2 mg once per day. After 4 weeks, your child’s doctor will check cholesterol levels and adjust the dosage as needed. The maximum dosage of Livalo for children is 4 mg per day.
Is Livalo taken long term?
Yes, Livalo is usually taken as a long-term treatment. If you and your doctor determine that it’s safe and effective for your condition, you’ll likely take it long term.
Dosage adjustments
In some situations, you may need a dosage adjustment for Livalo.
Your kidneys play an important role in removing Livalo from your body. If you have moderate to severe kidney problems or are on dialysis for end-stage kidney disease, the drug can build up in your body. This increases the risk of side effects. To prevent this, your doctor will likely prescribe a lower dosage of Livalo if you have kidney problems. For example, you may start on a dose of 1 mg once per day rather than the usual 2-mg dose.
Talk with your doctor if you have kidney problems and have questions or concerns about your Livalo dosage.
Below are answers to some commonly asked questions about Livalo’s dosage.
Does Livalo come as a generic? If so, is the dosage the same as the brand-name drug?
Yes, Livalo is available as the generic pitavastatin. It comes as a tablet and is available in the same strengths as Livalo.
The recommended dosages for the treatment of high cholesterol are the same for pitavastatin and Livalo.
If you have questions about how Livalo and its generic compare, talk with your doctor or pharmacist.
Is the dosage of Livalo similar to the dosage of Crestor or Lipitor?
Crestor (rosuvastatin), Lipitor (atorvastatin), and Livalo are all drugs called statins that come in tablet form. They’re available in multiple strengths. They’re usually taken once per day.
All are prescribed to decrease cholesterol, though how much of a decrease differs among the drugs, depending on the dose. Each drug is recommended at a dose that has proven to be effective in studies. Typical dosage ranges for the three drugs are as follows:
- Crestor: 5–40 milligrams (mg) per day
- Lipitor: 10–80 mg per day
- Livalo: 2–4 mg per day
If you have more questions about how Crestor, Lipitor, and Livalo compare, talk with your doctor or pharmacist.
The dosage of Livalo you’re prescribed may depend on several factors. These include:
- the type and severity of the condition you’re using the drug to treat
- other conditions you may have (see the “Dosage adjustments” section above)
Livalo comes as a tablet that you swallow. You’ll take it once per day. You can take the tablet with or without food.
Try to take your dose around the same time every day. This will help keep steady levels of Livalo in your blood.
Do not crush, cut, or chew the tablet. Swallow it whole. If you have trouble swallowing pills, see this article for tips on how to take this form of medication.
For information on the expiration, storage, and disposal of Livalo, see this article.
Accessible drug containers and labels
Some pharmacies provide medication labels that:
- have large print or use braille
- feature a code you can scan with a smartphone to change the text to audio
Your doctor or pharmacist may be able to recommend pharmacies that offer these accessibility features if your current pharmacy doesn’t.
If you have trouble opening medication bottles, let your pharmacist know. They may be able to supply Livalo in an easy-open container. They may also have tips to help make it simpler to open the drug’s container.
If you forget to take your usual daily dose of Livalo, take it as soon as you remember. But if it’s been more than 12 hours since the missed dose, skip the missed dose. Then take your next dose at the regularly scheduled time.
Do not take two doses of Livalo to catch up on a missed dose. This can increase your risk of side effects.
If you need help remembering to take your dose of Livalo on time, try using a medication reminder. This can include setting an alarm or downloading a reminder app on your phone.
Do not take more Livalo than your doctor prescribes, as this can cause harmful effects.
What to do in case you take too much Livalo
Call your doctor right away if you think you’ve taken too much Livalo. You can also call 800-222-1222 to reach America’s Poison Centers or use its online resource. But if you have severe symptoms, immediately call 911 (or your local emergency number) or go to the nearest emergency room.
The sections above describe the usual dosages provided by the drug’s manufacturer. If your doctor recommends Livalo for you, they’ll prescribe the dosage that’s right for you.
Remember, you should not change your dosage of Livalo without your doctor’s recommendation. Only take Livalo exactly as prescribed. Talk with your doctor if you have questions or concerns about your current dosage.
Here are some examples of questions you may want to ask your doctor:
- Does a higher dose of Livalo increase my risk of side effects?
- Would a lower dose of Livalo cost less?
- Will I need a new prescription if my dosage of Livalo is changed?
To get information on different conditions and tips for improving your health, subscribe to any of Healthline’s newsletters. You may also want to check out the online communities at Bezzy. It’s a place where people with certain conditions can find support and connect with others.
Disclaimer: Healthline has made every effort to make certain that all information is factually correct, comprehensive, and up to date. However, this article should not be used as a substitute for the knowledge and expertise of a licensed healthcare professional. You should always consult your doctor or another healthcare professional before taking any medication. The drug information contained herein is subject to change and is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, warnings, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or adverse effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a given drug does not indicate that the drug or drug combination is safe, effective, or appropriate for all patients or all specific uses.