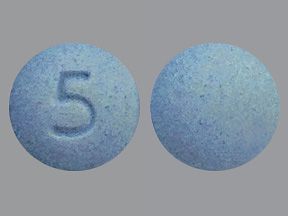
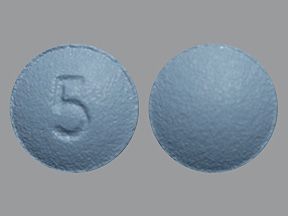
- Desloratadine oral tablet is available as a brand-name drug and a generic drug. Brand name: Clarinex.
- Desloratadine comes as a tablet, disintegrating tablet, and syrup. You take all forms by mouth.
- Desloratadine oral tablet is used to treat nasal and non-nasal symptoms of allergic rhinitis. It’s also used to relieve chronic itching caused by hives.
- Allergy warning: You shouldn’t use desloratadine if you’re allergic to it or any of its components. This drug can cause a hypersensitivity (allergic) reaction. This can lead to itching, rash, swelling, shortness of breath, and swelling of your lips, face, or tongue.
Desloratadine is a prescription drug. It comes in three forms: tablet, disintegrating tablet, and oral syrup. You take all forms by mouth.
Desloratadine is available as the brand-name drug Clarinex. It’s also available as a generic drug. Generic drugs usually cost less than the brand-name version. In some cases, they may not be available in every strength or form as the brand-name drug.
Why it’s used
Desloratadine oral tablet is used to treat nasal and non-nasal symptoms of seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis (allergies). It’s also used to help relieve chronic itching caused by hives.
How it works
Desloratadine belongs to a class of drugs called antihistamines. A class of drugs is a group of medications that work in a similar way. These drugs are often used to treat similar conditions.
Desloratadine works by blocking the release of a chemical called histamine from the cells in your body. This helps relieve symptoms of allergic rhinitis. These include sneezing, runny nose, and red, watery, and itchy eyes.
Desloratadine oral tablet may cause drowsiness. It can also cause other side effects.
More common side effects
Some of the more common side effects that can occur with use of desloratadine include:
- sore throat
- dry mouth
- muscle pain
- tiredness
- sleepiness
- menstrual pain
If these effects are mild, they may go away within a few days or a couple of weeks. If they’re more severe or don’t go away, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Serious side effects
Call your doctor right away if you have serious side effects. Call 911 if your symptoms feel life-threatening or if you think you’re having a medical emergency. Serious side effects and their symptoms can include the following:
- Allergic (hypersensitivity) reaction. Symptoms can include:
- skin rash
- itching
- hives
- swelling of your lips, tongue, face, and throat
Disclaimer: Our goal is to provide you with the most relevant and current information. However, because drugs affect each person differently, we cannot guarantee that this information includes all possible side effects. This information is not a substitute for medical advice. Always discuss possible side effects with a healthcare provider who knows your medical history.
Desloratadine oral tablet can interact with other medications, vitamins, or herbs you may be taking. An interaction is when a substance changes the way a drug works. This can be harmful or prevent the drug from working well.
To help avoid interactions, your doctor should manage all of your medications carefully. Be sure to tell your doctor about all medications, vitamins, or herbs you’re taking. To find out how this drug might interact with something else you’re taking, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Examples of drugs that can cause interactions with desloratadine are listed below.
Anti-infective drugs
When taken with desloratadine, some antibiotics can increase the amount of desloratadine in your body. This can cause more side effects. Examples of these drugs include:
- ketoconazole
- erythromycin
- azithromycin
Cholesterol drugs
When taken with desloratadine, some cholesterol drugs can increase the amount of desloratadine in your body. This can cause more side effects. Examples of these drugs include:
- atorvastatin
HIV and hepatitis C virus infection (HCV) drugs
When taken with desloratadine, some HIV and HCV drugs can increase the amount of desloratadine in your body. This can cause more side effects. Examples of these drugs include:
- ledipasvir
- lopinavir
- ombitasvir
- paritaprevir
- ritonavir
- saquinavir
Heart rhythm drugs
When taken with desloratadine, some heart rhythm drugs can increase the amount of desloratadine in your body. This can cause more side effects. Examples of these drugs include:
- dronedarone
Cancer drugs
When taken with desloratadine, some cancer drugs can increase the amount of desloratadine in your body. This can cause more side effects. Examples of these drugs include:
- tacrolimus
- tamoxifen
- sunitinib
- vandetanib
- vemurafenib
- lapatinib
Fluoxetine
When taken with desloratadine, fluoxetine can increase the amount of desloratadine in your body. This can cause more side effects. Talk to your doctor about whether this drug is safe for you.
Cimetidine
When taken with desloratadine, cimetidine can increase the amount of desloratadine in your body. This can cause more side effects. Talk to your doctor about whether this drug is safe for you.
Disclaimer: Our goal is to provide you with the most relevant and current information. However, because drugs interact differently in each person, we cannot guarantee that this information includes all possible interactions. This information is not a substitute for medical advice. Always speak with your healthcare provider about possible interactions with all prescription drugs, vitamins, herbs and supplements, and over-the-counter drugs that you are taking.
This drug comes with several warnings.
Allergy warning
Desloratadine can cause a severe allergic reaction. Symptoms can include:
- itching
- rash
- swelling anywhere in your body, especially in your lips, face, or tongue
- shortness of breath
If you develop these symptoms, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room.
Don’t take this drug again if you’ve ever had an allergic reaction to it. Taking it again could be fatal (cause death).
Food interaction warning
Grapefruit juice, grapefruit products, and the fruit grapefruit increase the amount of desloratadine in your body.
Alcohol interaction warning
The use of drinks that contain alcohol can increase your risk of drowsiness from desloratadine. If you drink alcohol, talk to your doctor.
Warnings for people with certain health conditions
For people with liver problems: If you have liver problems, you may not be able to process this drug properly. This puts you at a higher risk for side effects. Your doctor may prescribe a lower dosage of this drug.
For people with kidney problems: If you have kidney problems, you may not be able to clear this drug from your body properly. This puts you at a higher risk for side effects. Your doctor may prescribe a lower dosage of this drug.
Warnings for other groups
For pregnant women: Desloratadine is a category C pregnancy drug. That means two things:
- Research in animals has shown adverse effects to the fetus when the mother takes the drug.
- There haven’t been enough studies done in humans to be certain how the drug might affect the fetus.
Talk to your doctor if you’re pregnant or planning to become pregnant. This drug should be used only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk.
If you become pregnant while taking this drug, call your doctor right away.
For women who are breastfeeding: Desloratadine passes into breast milk and may cause side effects in a child who is breastfed. Talk to your doctor if you breastfeed your child. You may need to decide whether to stop breastfeeding or stop taking this medication.
For seniors: Older adults may process drugs more slowly. A typical adult dosage may cause levels of the drug to be higher than normal in your body.
For children: This drug hasn’t been proven to be safe and effective in children younger than 6 months. It shouldn’t be used in children younger than 6 months.
All possible dosages and drug forms may not be included here. Your dosage, drug form, and how often you take the drug will depend on:
- your age
- the condition being treated
- how severe your condition is
- other medical conditions you have
- how you react to the first dose
Drug forms and strengths
Generic: Desloratadine
- Form: oral tablet
- Strength: 5 mg
- Form: oral disintegrating tablet
- Strengths: 2.5 mg, 5 mg
Brand: Clarinex
- Form: oral tablet
- Strength: 5 mg
- Form: orally disintegrating tablet
- Strengths: 2.5 mg, 5 mg
- Typical dosage for both tablets: One 5-mg tablet once per day.
- Typical dosage for both tablets: One 5-mg tablet once per day.
- Typical dosage for disintegrating tablets:
- Ages 6 years to 11 years: One 2.5-mg tablet once per day.
- Ages 6 months to 5 years: It hasn’t been confirmed that this form is safe and effective for this age group.
- Other forms: Children ages 6 months to 11 years are advised to use the oral syrup instead of the oral tablet.
- Typical dosage for both tablets: One 5-mg tablet once per day.
- Typical dosage for both tablets: One 5-mg tablet once per day.
- Typical dosage for disintegrating tablets:
- Ages 6 years to 11 years: One 2.5-mg tablet once per day.
- Ages 6 months to 5 years: It hasn’t been confirmed that this form is safe and effective for this age group.
- Other forms: Children ages 6 months to 11 years are advised to use the oral syrup instead of the oral tablet.
- Typical dosage for both tablets: One 5-mg tablet once per day.
- Typical dosage for both tablets: One 5-mg tablet once per day.
- Typical dosage for disintegrating tablets:
- Ages 6 years to 11 years: One 2.5-mg tablet once per day.
- Ages 6 months to 5 years: It hasn’t been confirmed that this form is safe and effective for this age group.
- Other forms: Children ages 6 months to 11 years are advised to use the oral syrup instead of the oral tablet.
- You can take desloratadine with or without food.
- You can cut or crush the regular tablets. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you can cut or crush your tablets.
- Store desloratadine tablets at room temperature. Keep them at a temperature between 59°F and 86°F (15°C and 30°C).
- Keep them away from high temperatures (above 86°F). They are sensitive to heat.
- Don’t store this medication in moist or damp areas, such as bathrooms.
- Always carry your medication with you. When flying, never put it into a checked bag. Keep it in your carry-on bag.
- Don’t worry about airport X-ray machines. They can’t harm your medication.
- You may need to show airport staff the pharmacy label for your medication. Always carry the original prescription-labeled container with you.
- Don’t put this medication in your car’s glove compartment or leave it in the car. Be sure to avoid doing this when the weather is very hot or very cold.