Pustules, or pus-filled bumps, can occur due to acne, an allergic reaction, or an infection. If they occur alongside additional symptoms, such as fever or extreme pain, you may need urgent medical attention.
Pustules are small bumps on the skin that contain fluid or pus. They usually appear as white bumps surrounded by red or inflamed skin.
Pustules may develop on any part of the body, but they most commonly form on the back, chest, and face. They may be found in clusters on the same area of the body.
Pustules are typically caused by acne, a very common skin condition, particularly among teenagers and young adults.
Small pustules typically go away without treatment. However, more severe pustules may require prescription acne medications.
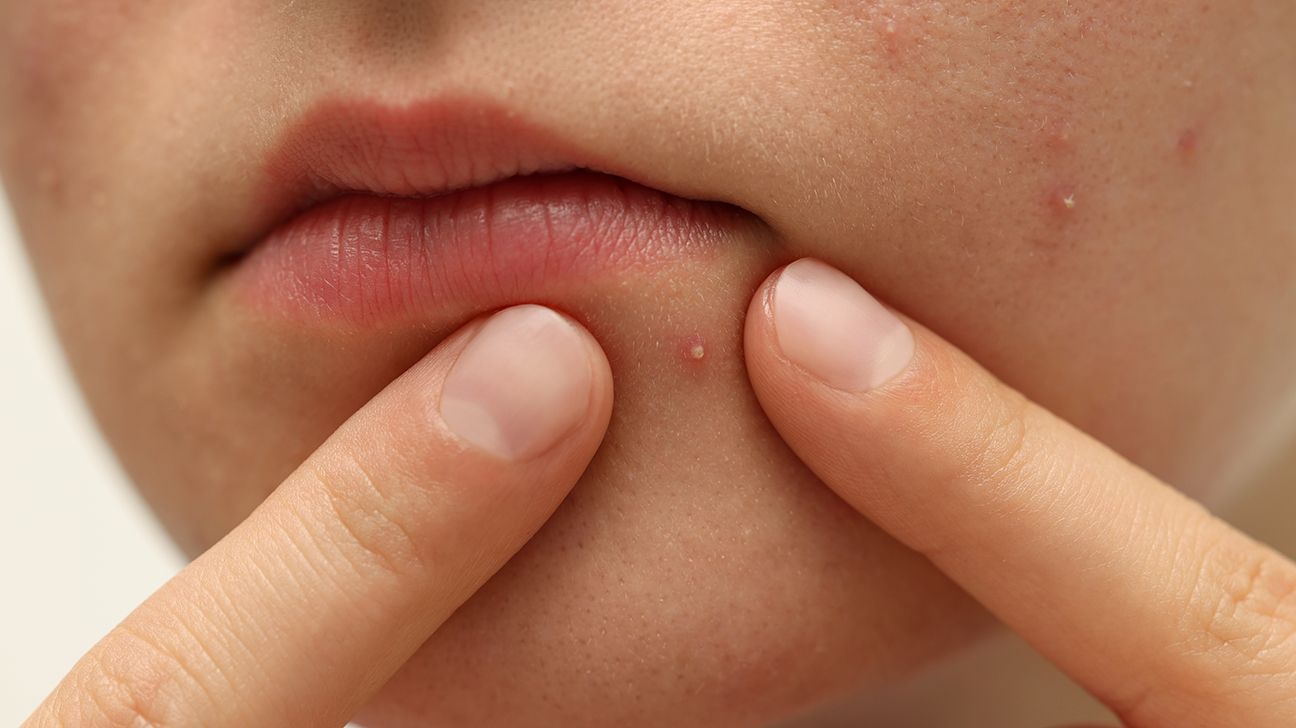
Pustules are easy to identify. They appear as small bumps on the surface of your skin. The bumps usually have white or red edges with a white or yellow center. They may be inflamed and painful to the touch. The skin around the acne may appear red for light skin tones and resemble dark spots for dark skin tones.
Pustules commonly occur on the following body areas:
Pustules may form when the skin becomes inflamed due to an allergic reaction to food, environmental allergens, or poisonous insect bites.
However, the most common cause of pustules is acne. Acne can develop due to hormonal imbalances in the body and result in skin pores becoming clogged with oil and dead skin cells.
This blockage causes patches of skin to bulge, resulting in a pustule.
Pustules usually contain pus due to an infection of the pore cavity. Pustules caused by acne can become hard and painful. When this occurs, the pustule becomes a cyst. This condition is known as cystic acne.
Pustules that suddenly erupt all over your face or in patches on various parts of your body may indicate that you have a bacterial infection. You should speak with a doctor as soon as possible if you have a sudden outbreak of pustules.
You should also speak with a doctor if your pustules are painful or leaking fluid. These may be symptoms of a serious skin infection.
If you experience any of the following symptoms along with pustules, you should go to the nearest emergency room immediately:
- fever
- warm skin in the pustule-affected area
- clammy skin
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- pain in the area containing the pustules
- large pustules that are extremely painful
Small pustules typically go away without treatment. If small pustules persist, it can be helpful to wash your skin with warm water and a mild cleanser. Doing this twice per day can help remove any oil buildup, which is the main cause of acne.
It can help to gently use your fingertips instead of a washcloth to cleanse your face. Scrubbing pustules with a washcloth may further irritate your skin.
Pustules can be treated using over-the-counter (OTC) acne medications, soaps, or creams. The best topical products for treating pustules contain peroxide, salicylic acid, and sulfur. However, these treatments should never be used in your genital area.
OTC products help treat pustules by drying the top layer of skin and absorbing excess surface oils. Some products are strong and may cause your skin to become extremely dry and peel. If you have sensitive skin, consider choosing products specially made for your skin type so your condition doesn’t worsen.
Avoiding oil-based products, such as lotions or petroleum jelly, in the pustule-affected areas can also be beneficial. These products can further block your pores and cause symptoms to worsen.
Read more about acne treatment.
If you find that your pustules are not improving with home remedies and OTC treatments, consider speaking with a dermatologist, who can suggest more effective treatment options. They may be able to drain your pustules safely or prescribe a stronger medication.
Prescription medications can be very useful in eliminating acne pustules, especially those caused by bacterial infections. Common medications a doctor may prescribe include:
- oral antibiotics, such as doxycycline and amoxicillin
- topical antibiotics, such as dapsone
- prescription-strength salicylic acid
In severe cases, a procedure called photodynamic therapy (PDT) may be
PDT is a treatment that combines light and a special light-activated solution that targets and destroys acne. Aside from eliminating pustules and other related skin conditions caused by acne, PDT may also diminish older acne scars and make your skin smoother.
Consider speaking with a dermatologist to see whether PDT may be suitable for treating your condition.
Should you pop a pustule?
It is generally advised not to pop a pustule. While it may be tempting to remove your pustules by popping them, you should not squeeze, pick, or pinch them. Doing so can damage your skin or make the infection worse.
Is a pustule the same as a pimple?
Pustules are a type of pimple. They can occur due to an infection and clogging of the pore cavity. This can cause patches of skin to bulge and fill with pus.
How do you get rid of pustules?
You can get rid of pustules by gently washing your skin using a mild facial cleanser twice a day. Persistent or severe pustules can be treated using acne medications, soaps, or creams. A dermatologist can help you identify the most suitable treatment option for your individual needs.
Pustules are small pus-filled bumps that commonly develop in areas such as the shoulders, back, and face. They can be painful to the touch and may cause the surrounding skin to become inflamed.
The most common cause of pustules is acne. An allergic reaction to food, environmental allergens, or poisonous insect bites can also cause pustules.
Small pustules typically go away without treatment. However, larger and more severe pustules may require prescription acne medications.
If you find that your pustules are not improving, consider speaking with a dermatologist. They can put together a treatment plan based on your individual needs.
